
Imagine waking up to find your entire system locked, critical files encrypted, and a demand for a hefty ransom flashing on your screen. Ransomware attacks are evolving alarmingly, and 2025 is the worst year yet for cyber extortion. Hackers leverage AI-powered malware, sophisticated phishing techniques, and unpatched vulnerabilities to launch relentless cyberattacks against businesses and individuals.
By 2025, ransomware attacks will occur every 11 seconds, with global damages exceeding $265 billion annually. The question is no longer if an attack will happen but when.
Are you prepared? Ransomware defense is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. Let’s dive into the rising threats and essential measures you must take to protect your data safety, financial assets, and digital identity.
Ransomware: A Rising Threat of 2025
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts files and locks you out of your system. Cybercriminals then demand payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for a decryption key. Paying the ransom is no guarantee of recovery, and in many cases, victims never regain access to their data.
The modern ransomware attack doesn’t just lock files—it steals sensitive data before encrypting it. This means even if you have backup software, hackers can still leak your confidential information on the dark web, causing data breaches and reputational damage.
Types of Ransomware Attacks in 2025
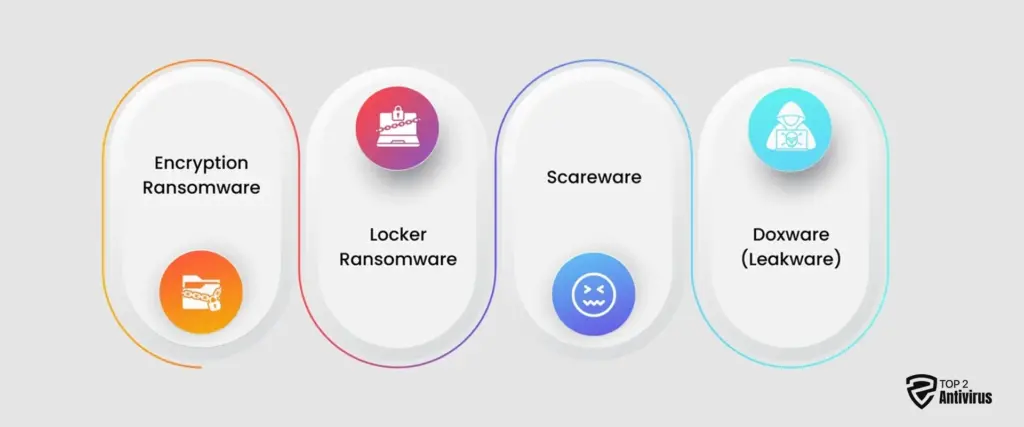
Hackers have developed several forms of ransomware to maximize damage. Here are the most common types:
1. Encryption Ransomware
- The most common attack method is to encrypt your files, making them unreadable.
- Only the hacker-controlled decryption key can restore access.
- Without proper ransomware protection, recovery is nearly impossible.
2. Locker Ransomware
- It prevents access to your entire system, making computers and networks unusable.
- The only way to regain access is by paying the ransom or restoring from backup software.
3. Scareware
- Displays fake security alerts, tricking users into downloading malicious security software.
- Users are forced to pay for phony virus protection while hackers steal data in the background.
4. Doxware (Leakware)
- Threatens to leak sensitive personal or corporate data unless the ransom is paid.
- Businesses dealing with confidential client data are top targets for this attack.
Ransomware Attacks: What are the Entry Points?
Cybercriminals exploit multiple attack vectors to infiltrate systems. The most common entry points include:
- Phishing Emails: Fake messages impersonating legitimate sources trick users into clicking malicious links.
- Unpatched Software: Hackers exploit vulnerabilities to gain access without real-time security updates.
- Malicious Websites: Clicking on infected ads or downloading files from untrusted sources introduces ransomware.
- Public Wi-Fi Attacks: Hackers intercept unsecured Wi-Fi connections, injecting malware into devices.
- Compromised Credentials: Stolen passwords lead to complete system takeovers, enabling data encryption and extortion.
- Hackers are more advanced than ever. Ransomware protection and anti-ransomware tools are essential for businesses and individuals.
Internet Security Solutions of 2025
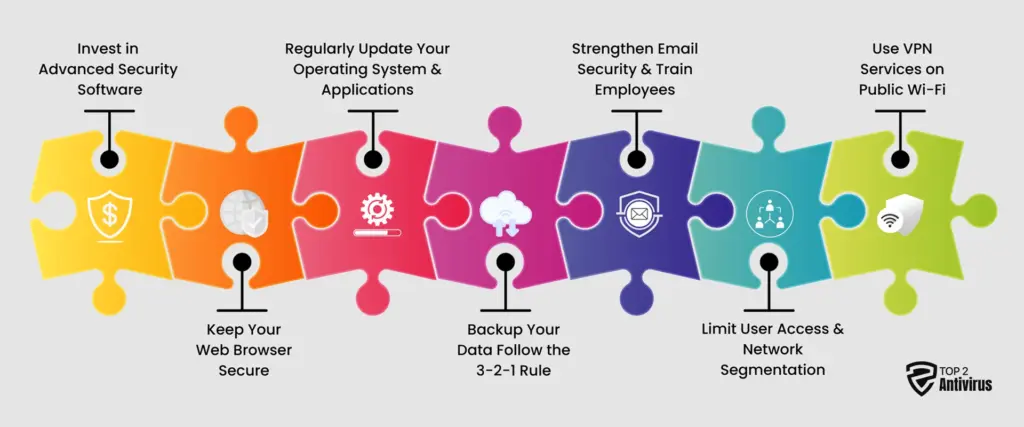
To stay ahead of cybercriminals, you must implement comprehensive cybersecurity strategies that offer real-time protection. Here’s how:
Invest in Advanced Security Software
- Use AI-powered security software with intrusion detection to stop attacks before they execute.
- Enable real-time security monitoring to detect threats as they emerge.
- Deploy endpoint security solutions to protect all connected devices from infiltration.
Keep Your Web Browser Secure
- Regularly update web browser security settings to block malicious sites.
- Avoid downloading extensions or software from unverified sources.
- Use browser-based real-time protection to prevent phishing attempts and drive-by ransomware attacks.
Regularly Update Your Operating System & Applications
- Hackers exploit outdated software—keep everything updated to eliminate vulnerabilities.
- Enable automatic system updates, including virus scanners, backup software, and Internet security solutions.
Backup Your Data—Follow the 3-2-1 Rule
- Maintain three copies of your data for redundancy.
- Store data across two different storage types to prevent loss.
- Keep one copy offline or in immutable cloud storage for extra protection.
- Utilize backup software to ensure quick recovery from ransomware attacks.
Strengthen Email Security & Train Employees
- Implement anti-ransomware tools that filter out phishing emails.
- Train employees to recognize social engineering attacks and avoid clicking on suspicious links.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent credential theft.
Limit User Access & Network Segmentation
- Zero-trust security ensures no one has more access than necessary.
- Network segmentation isolates infected systems, preventing ransomware attacks from spreading.
Use VPN Services on Public Wi-Fi
- Public Wi-Fi is a hacker’s playground—use VPN encryption to protect your data.
- Incorporate Internet security solutions with real-time protection to prevent unauthorized access.
What to Do After a Ransomware Attack?
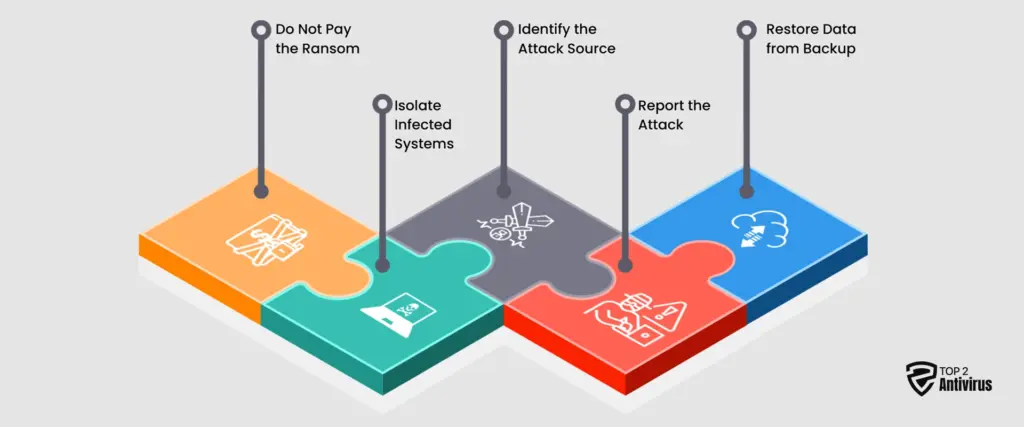
Falling victim to a ransomware attack can be devastating, but taking the proper steps immediately can help minimize the damage and prevent further infections. Acting quickly and decisively is crucial in recovering your data while strengthening your security for the future.
1. Do Not Pay the Ransom
Paying the ransom may seem the easiest way to regain access to your files, but it does not guarantee data recovery. Many victims never receive a working decryption key, even after payment. Additionally, giving in to ransom demands only encourages cybercriminals to continue their attacks, funding illegal activities and increasing the risk of future ransomware attacks. Instead of paying, focus on recovery efforts using backup software and professional cybersecurity solutions.
2. Isolate Infected Systems
When you identify a ransomware infection, immediately disconnect the affected system from Wi-Fi, local networks, and cloud storage. This helps contain the attack and prevents ransomware from spreading to other devices within your network. If an organization is under attack, isolating compromised devices should be the top priority to prevent further data loss and reduce the impact on other business operations.
3. Identify the Attack Source
Understanding how the ransomware entered your system is essential for strengthening cybersecurity and preventing future attacks. Utilize intrusion detection tools to analyze where the malware originated. Whether through a phishing email, a malicious download, or an unpatched vulnerability, identifying the source will help you implement targeted security measures to block similar threats in the future.
4. Report the Attack
Contact law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity experts as soon as possible to investigate the attack. Many government cybersecurity organizations offer free decryption tools for known ransomware variants, which could help you recover your data without paying a ransom. Reporting the incident can also contribute to ongoing efforts to track cybercriminals and prevent further ransomware activities.
5. Restore Data from Backup
If you have backup software, restore your system from a clean, pre-attack backup to recover lost files. Cloud-based immutable backups ensure that even if ransomware encrypts local files, a secure copy of your data remains untouched. Regularly updating and testing backup systems is essential to ensure data recovery is possible without relying on ransom payments.

Ransomware Defense: Real-Time Protection Needed
By investing in endpoint security, virus protection, real-time security, and intrusion detection, you can create resilience against cyber threats that breach your security. It’s time to use advanced backup software for data safety and provide training to employees to create a strong shield against ransomware. To prevent a ransomware attack in 2025, take a smart move and deploy AI-driven security options.



